Describe the Structure of an Enzyme
The enzyme chains fold over to form unique shapes and it is these shapes that provide the enzyme with its characteristic chemical potential. This suggested that the enzymes shape was being altered by the binding molecule.

As Biology Daily Revision Task 36 Enzyme Activity Enzymes Activity Biology Biology Revision
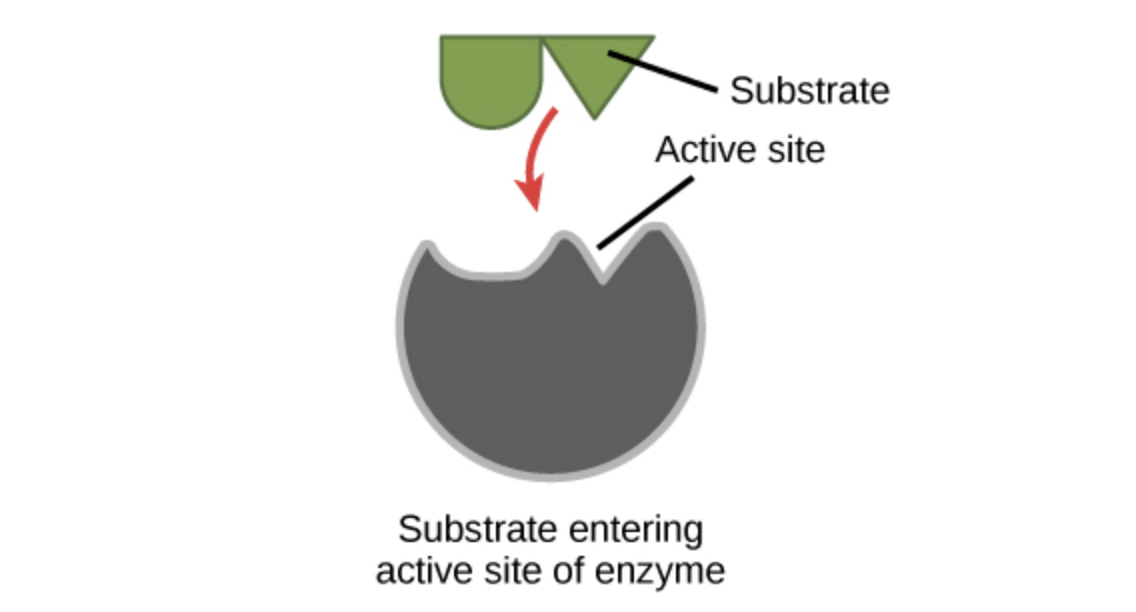
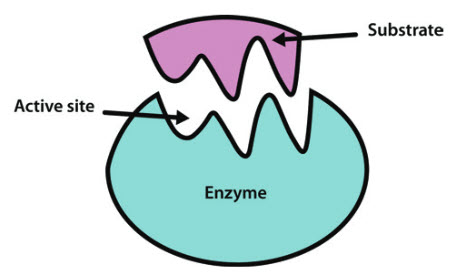
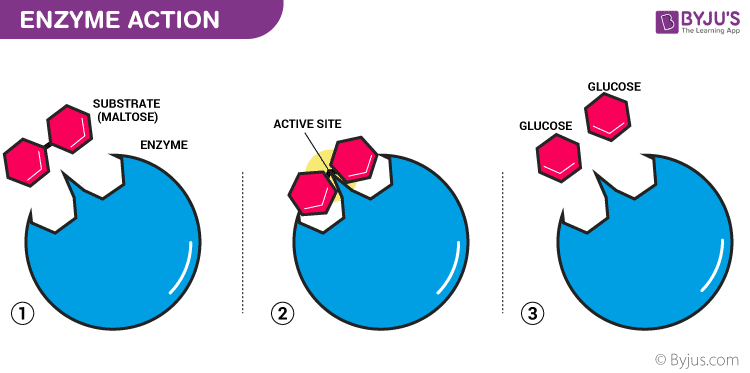
For an enzyme-mediated chemical reaction to occur the shape and charge of the substrate must be compatible with the active site of the enzyme.
. All enzymes are made up of proteins but all proteins are not enzymes. The structure of amylase an enzyme that breaks down starches and complex sugars into simple sugars is usually quite simple but the enzyme plays an important role in digestion of carbohydratesThere are two different variations of this molecule. Their folded chains of amino acids can be represented by simple shapes.
They help in generating. Enzymes are actually made up of 1000s of amino acids that are linked in a specific way to form different enzymes. The enzyme has about 12 β-conformation and 40-α helical segments.
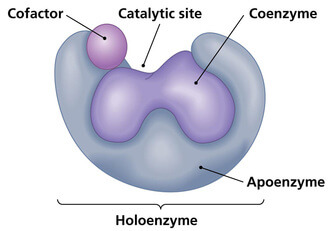
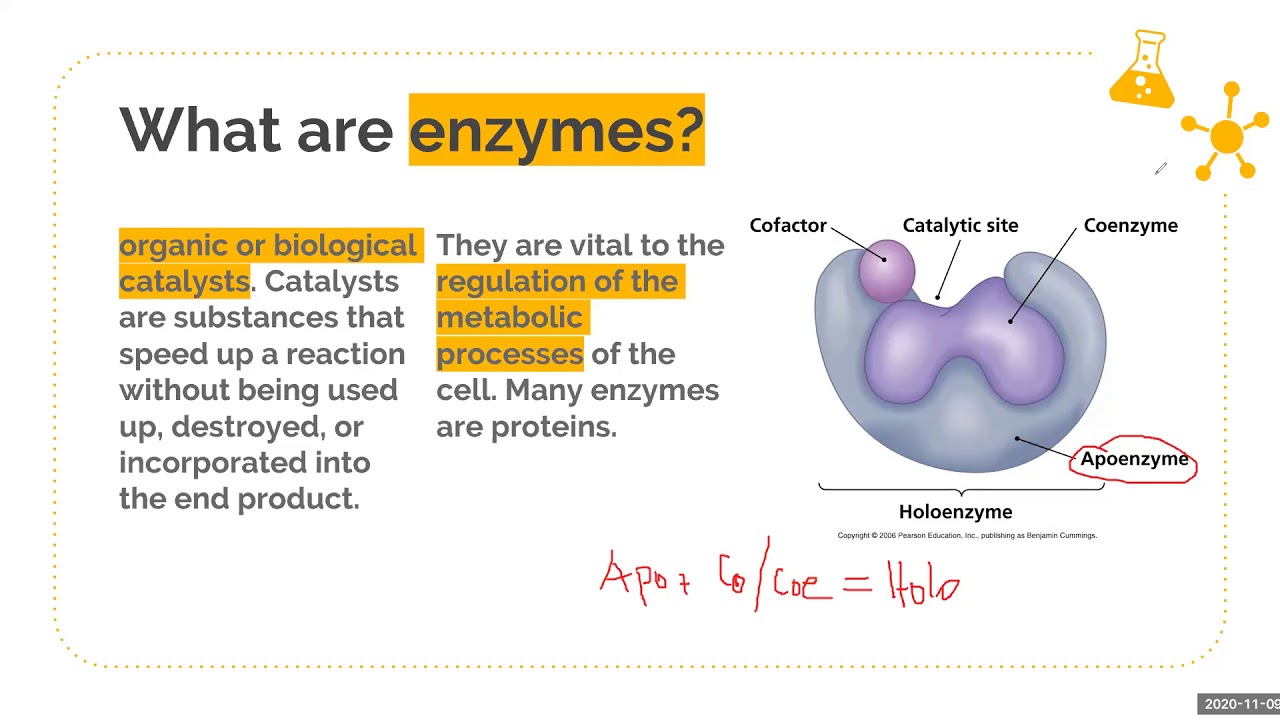
The co-factors are of three types. In many enzymes there is found a non-protein part associated with protein. What is the role of haemoglobin.
This is the currently selected item. Co-factors co-enzymes and vitamins. It is the location where substrate molecules are produced.
In many enzymes there is found a non-protein part associated with protein. Ø Some enzymes require no chemical groups for activity other than their amino acid residues. Describe the structural properties of a globular protein.
What organ secretes insulin. In the lock and key model the enzyme was considered to be a rigid structure. Such enzymes are known as conjugated enzymes or holoenzymes.
Enzymes help in signal transduction. Enzymes are proteins that consist of chains of amino acids connected together by peptide bonds. The enzyme lysozyme is consists of 129 amino acids linked together to form the primary structure and the first amino acid is lysine.
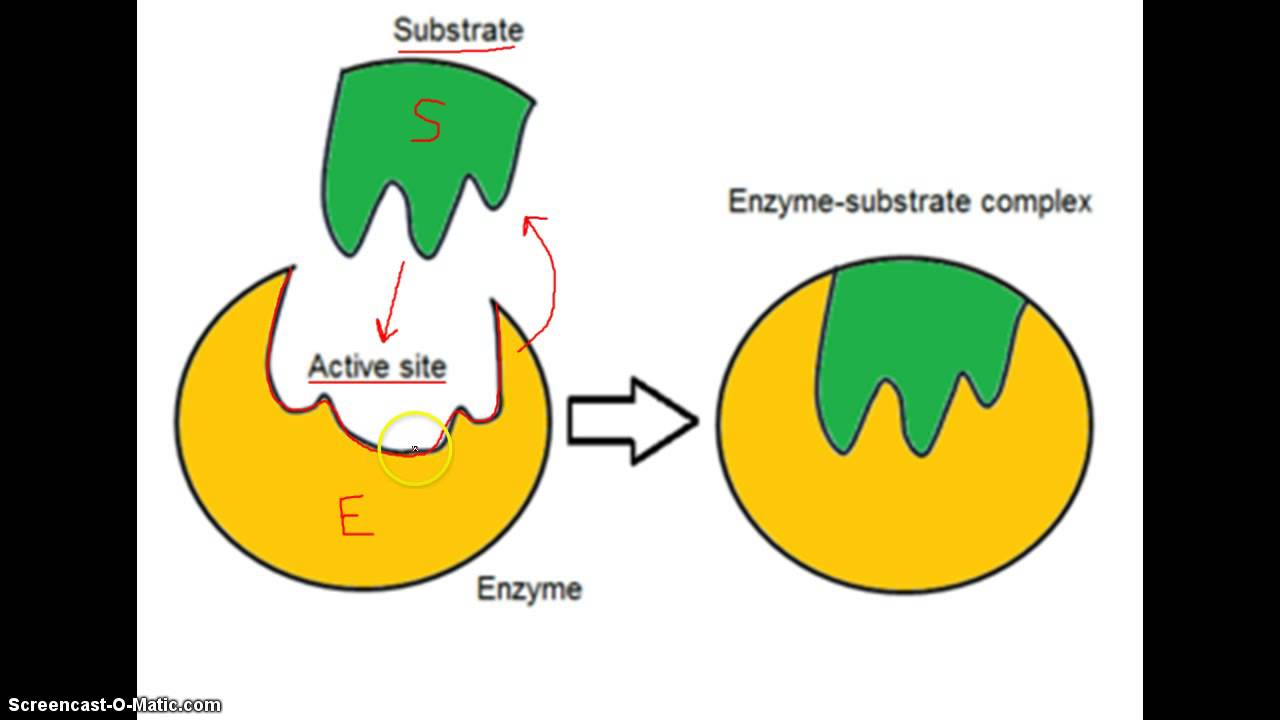
Describe the structure of amylase. The specific order of amino acid in the protein is encoded by the DNA sequence of the corresponding gene. For many years scientists thought that enzyme-substrate binding took place in a.
However scientists observed that other molecules could bind to enzymes at site other than the active site. It always accommodates several structurally related substrates. It always has a geometrical shape exactly complementary to that of substrate.
Introduction to enzymes and catalysis. The protein part of the conjugated enzyme is called apoenzyme. Enzymes made of protein polypeptide chains of amino acids have specific shape work with one type of substrate can work on catabolic braking or anabolic building reactions active site region of enzyme where substrate binds allosteric site region of whee non-substrate molecules can bind to regulate enzyme function enzyme substrate complex.
The most common enzyme used in the process includes protein kinase that catalyzes the phosphorylation of proteins. Indicate whether each of the following statements about an enzyme active site is true or false. Induced fit model of enzyme catalysis.
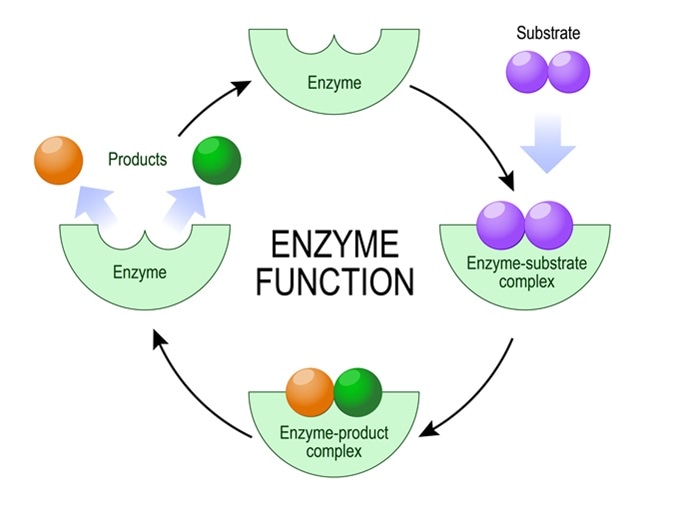
While they hasten or speed up a process they are actually providing an alternative pathway for the process. Enzyme Structure And Function. - enzyme binds to the reactants called the substrates of a chemical reaction - the substrate joins with the enzyme at the enzymes active site forming an enzyme-substrate.
Enzymes are specialized proteins that speed up chemical reactions biological catalysts Without enzymes cellular chemical reactions could not occur fast enough to maintain life. Amino acids are linked by hydrogen bonds with various chemical groups attached to give enzymes their two dimensional shape Amino acids are linked by hydrogen bonds with various chemical. The protein part of the conjugated enzyme is called apoenzyme.
The enzyme chains fold over to form unique shapes and it is. Most enzymes also contain a non-protein component known as the co-factor. 2-16 comprises 2 nucleotides one consisting of adenine ribose and phosphate and the other nicotinamide ribose and phosphate linked by a pyrophosphate bond.
Describe the structure of haemoglobin. Its structure see fig. Enzyme structure and function.
It always has a fixed rigid geometry. Jessica Susan Reuter Date. Six types of enzymes.
April 03 2022 Amylase is an enzyme that breaks down starch and it is secreted in saliva. Enzymes are actually made up of thousands of amino acids that are linked in a specific way to form different enzymes. Ø Others enzymes require additional chemical components one or more for their activity.
Such enzymes are known as conjugated enzymes or holoenzymes. Describe the properties of enzymes. Induced-Fit Model of Enzymes.
The nonprotein part of the conjugated enzyme is called cofactor. Many enzymes are made up exclusively of protein and such enzymes are called simple enzymes. What is a globular protein.
Ø Most of the enzymes consist of multi-subunits more than one polypeptide chains. The resulting amino acid chain is called a polypeptide or protein. Describe the structure of insulin.
Ø Enzymes are much larger than their substrates. What does it mean to be a conjugated protein. An enzyme molecule may have one or more of these polypeptide chains.
Structure of Enzymes Primary structure Enzymes are made up of amino acids which are linked together via amide peptide bonds in a linear chain. Select all of the following that can be used to describe the structure of enzymes the importance of the shape and the relationship of enzyme shape and function. 31 Enzyme Structure Overview.
What is the role of insulin. Enzymes and activation energy. But in the process the structure or composition of the enzymes remain unaltered.
In doing so they altered the activity of the enzyme. This is the primary structure. The structure of enzymes includes the active site that specifically interacts with substrate molecules.
Functions of Enzymes. The induced-fit model proposes that the initial interaction between enzyme and substrate is relatively weak but that these weak interactions rapidly induce conformational changes in the enzyme that strengthen binding. The sequence of amino acids within the polypeptide chains is distinct in each enzyme and this is what determines the unique three-dimensional shape in which the chains are folded.
They break down large molecules into smaller substances that can be easily absorbed by the body.

Enzyme Structure And Function Mini Project Structure And Function Student Reading Student Studying

What Is A Lysosome Structure Function And Storage Diseases Eukaryotic Cell Organelles Structure And Function
What Two Components Are Often Found As Part Of An Enzyme Lisbdnet Com

Lock And Key Model Is Used To Describe The Mechanism Of Enzyme Action This Model Was First Proposed By German Chemist Emil Fisher In 2021 Biology Lesson Video Lessons

Enzymes Definition Structure Types Mode Of Action Functions

Structure And Function Of Vacuole Types With Examples In 2021 Structure And Function Plant Cell Biology

Enzymes And Temperature Guided Notes Worksheets Editable Enzymes Activity Guided Notes Enzymes
What Two Components Are Often Found As Part Of An Enzyme Lisbdnet Com
Chapter 6 Enzyme Principles And Biotechnological Applications Chemistry

Cloze Worksheet Enzymes Biology 9 12 Enzymes Biology Biology Worksheet Biology Lessons

Enzymes Review Article Khan Academy
Enzymes Structure Classification And Function

Free Lab Catalase An Enzyme Common To Both Plants And Animals Biology Classroom Biology Labs Biology

Enzyme Review Worksheet Answers Luxury Enzyme Annotation Worksheet By Aaron Chandler Teaching Biology Activity Biology Lessons Teaching Biology